



CHINESE DENTAL HISTORY
Copyright 2022 © Chinese American Dental Association. All Right Reserved



BLOG






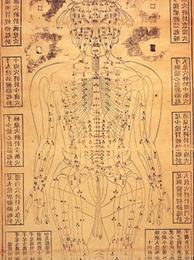
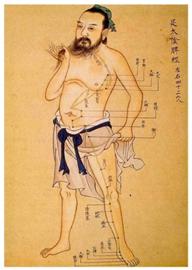
Acupuncture More than 360 pointson the surface of the body that are thought by the Chinese
to be directly linked with the internal structures have been charted. A number of
these points - 116 in all - are believed to be connected with the teeth and other
oral structures, and acupuncture treatment of oral ailments has proven singularly
effective. It is used widely in multiple tooth extractions as well as in the treatment
of gingivitis, stomatitis, and glossitis.

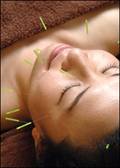
Moxibustion Moxibustion is used widely, along with acupuncture, for
treatment of toothache and other oral ills.
Moxibustion is a traditional Chinese medicine technique that involves the
burning of mugwort, a small, spongy herb, to facilitate healing. Suppliers
usually age the mugwort and grind it up to a fluff; practitioners burn the fluff
or process it further into a stick that resembles a (non-smokable) cigar.
They can use it indirectly, with acupuncture needles, or sometimes burn it
on a patient's skin. The burning of moxa or other substances on the skin to
treat diseases or to produce analgesia. The purpose of moxibustion, as with
most forms of traditional Chinese medicine, is to strengthen the blood,
stimulate the life energy or qi, and maintain general health.
treatment of toothache and other oral ills.
Moxibustion is a traditional Chinese medicine technique that involves the
burning of mugwort, a small, spongy herb, to facilitate healing. Suppliers
usually age the mugwort and grind it up to a fluff; practitioners burn the fluff
or process it further into a stick that resembles a (non-smokable) cigar.
They can use it indirectly, with acupuncture needles, or sometimes burn it
on a patient's skin. The burning of moxa or other substances on the skin to
treat diseases or to produce analgesia. The purpose of moxibustion, as with
most forms of traditional Chinese medicine, is to strengthen the blood,
stimulate the life energy or qi, and maintain general health.



Oral Medicine

ADA website
Malvin E. Ring, DDS. Dentistry: An Illustrated History. Mosby- Year Book.
Malvin E. Ring, DDS. Dentistry: An Illustrated History. Mosby- Year Book.
18th Century Further advances were made in understanding oral disease and oral anatomy.
Between 1784 and 1826, Chao wen-tsin compiled a major work on surgery in
which numerous instruments for operations in the mouth were depicted.
In 1822, an important medical treatise ( Illustrated Notes of Symptoms and
Treatment in Laryngology) contained an extensive description of oral anatomy).
It contains a detailed description of the oral structures and defines the division
between the oral cavity and the pharynx. The work also includes articles on mouth
and throat abscesses as well as tumors of the
Between 1784 and 1826, Chao wen-tsin compiled a major work on surgery in
which numerous instruments for operations in the mouth were depicted.
In 1822, an important medical treatise ( Illustrated Notes of Symptoms and
Treatment in Laryngology) contained an extensive description of oral anatomy).
It contains a detailed description of the oral structures and defines the division
between the oral cavity and the pharynx. The work also includes articles on mouth
and throat abscesses as well as tumors of the

Oral Medicine

300 B.C. Tongue examination was first described in the Nei Ching (Canon of Medicine).
The technique used today remains essentially unchanged: color, coating, and
moistness of the tongue are all carefully noted as an aid to diagnosis. Changes
in the appearance of the tongue are believed to reflect disease and to indicate
the severity and suggest prognosis of the condition.
A.D 25- 220 Hua Shou ( a great diagnostician), in his commentary
on the Nan Ching described the whitish spots in the
mouth that are the premonitory symptom of measles.

11 th Century T’ing To-t’ung and Yu Shu described the entire
process of mastication and deglutition.
process of mastication and deglutition.
255- 206 B.C. Cleft lip repair was described in an ancient monograph during the Ch’in dynasty.
(The earliest report of such surgery anywhere in the world)
(The earliest report of such surgery anywhere in the world)

17 th A.D Chinese surgeons were familiar with many diseases of the mouth and throat and
undertook treatment of such conditions as tonsillar abscesses and eptheliomas of
the lip.
undertook treatment of such conditions as tonsillar abscesses and eptheliomas of
the lip.



These beautiful Chinese toilet sets of silver and ivory include toothpicks as
well as tweezers and ear scoops
well as tweezers and ear scoops
Oral Medicine

2nd Century A.D Chinese used arsenic to treat decayed teeth ( probably to kill the
pulp and relieve the pain of toothache ) .

Twelfth Century Other early writings indicate that full dentures were being onstructed .
2nd Century A.D Chinese used arsenic to treat decayed teeth ( probably to kill the
pulp and relieve the pain of toothache ) .
When Marco Polo traveled to China in 1270s, he found that Chinese have
the custom of covering their teeth with thin piece of gold plates.

* Chewstick for cleaning teeth was apparently
borrowed from the Chinese and Babylonians.
borrowed from the Chinese and Babylonians.

2nd Century A.D Chinese used arsenic to treat decayed teeth ( probably to kill the
pulp and relieve the pain of toothache ) .
A.D 659 Chinese developed a type of silver amalgam for filling more than a
thousand years before dentists in the West .
thousand years before dentists in the West .

Li Shih-Chen
“Silver Paste”is mentioned in the material medica of Su Kung (A.D 659).
During the Ming period, Liu Wen-t’ai (1505) and Li Shih-Chen (1578) discuss its formulation: 100 parts of mercury to 45 parts of silver and 900 parts of tin. Trituration of these ingredients produced a paste said
to be as solid as silver.
“Silver Paste”is mentioned in the material medica of Su Kung (A.D 659).
During the Ming period, Liu Wen-t’ai (1505) and Li Shih-Chen (1578) discuss its formulation: 100 parts of mercury to 45 parts of silver and 900 parts of tin. Trituration of these ingredients produced a paste said
to be as solid as silver.
DENTAL HISTORY HIGHLIGHTS IN
CHRONOLOGICAL ORDER
CHRONOLOGICAL ORDER
(The great Sung landscapist Li T’ang depicts a
country doctor cauterizing a patient’s arm by burning
it with the powdered leaves of an aromatic plant. The
treatment is called Moxibustion , which is widely
used along with acupuncture for treatment such as
relieving toothache.)
country doctor cauterizing a patient’s arm by burning
it with the powdered leaves of an aromatic plant. The
treatment is called Moxibustion , which is widely
used along with acupuncture for treatment such as
relieving toothache.)
History
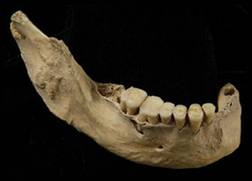
Historical evidence proves that dentistry started around the areas of China,
Egypt, India, Etruscans of Central Italy, Assyrians, and Japan.
Egypt, India, Etruscans of Central Italy, Assyrians, and Japan.


(The great Sung landscapist Li T’ang depicts a country doctor cauterizing a patient’s
arm by burning it with the powdered leaves of an aromatic plant. The treatment is
called Moxibustion , which is widely used along with acupuncture for treatment such as relieving toothache.)
arm by burning it with the powdered leaves of an aromatic plant. The treatment is
called Moxibustion , which is widely used along with acupuncture for treatment such as relieving toothache.)

2700 BC Chinese used acupuncture to treat pain associated with tooth decay.

